What is a Hybrid Car and How Do They Work?
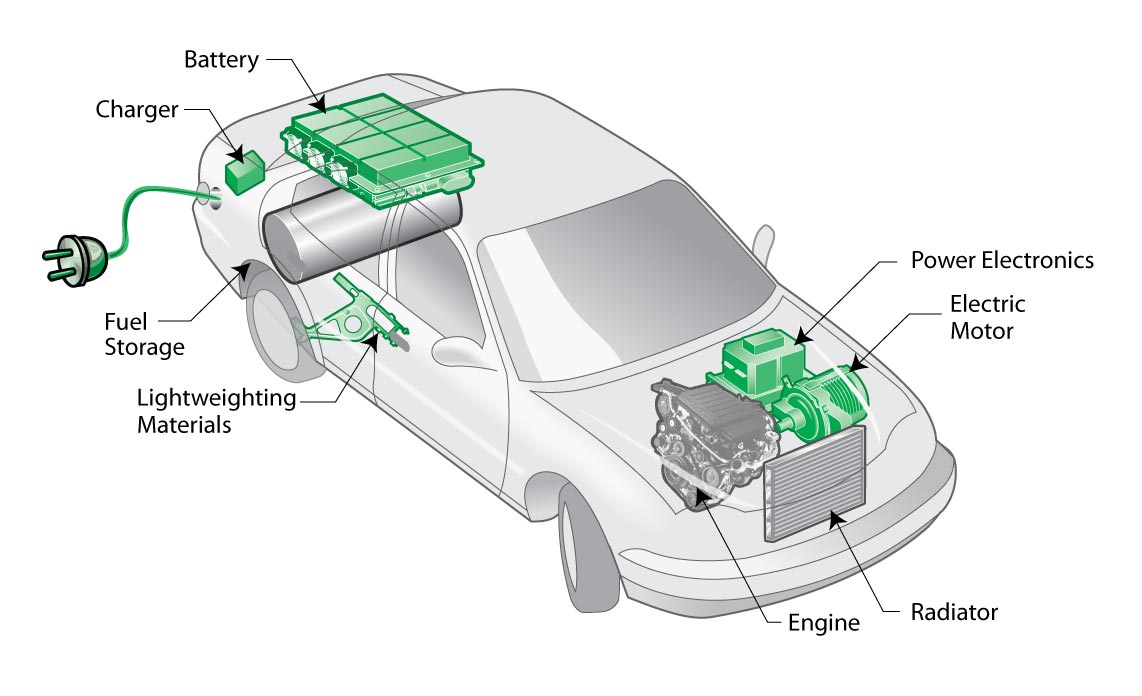
A hybrid engine is a type of engine that combines two or more energy sources to power a vehicle or machine. The most common type of hybrid engine is the hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) engine, which combines an electric motor and a gasoline engine to drive the wheels.
In HEVs, the electric motor is used to propel the vehicle at low speeds, while the gasoline engine kicks in when more power is needed, such as when accelerating or climbing hills. The electric motor also acts as a generator and uses regenerative braking to convert some of the energy lost during braking into electricity to charge the battery.
Other types of hybrid engines include diesel-electric hybrids, which combine a diesel engine with an electric motor, and hydrogen fuel cell hybrids, which use a hydrogen fuel cell in combination with an electric motor.
Contents
What is a hybrid?
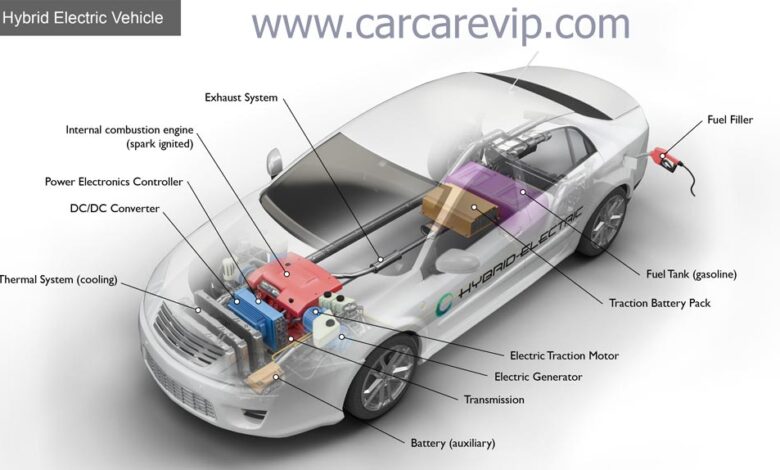
A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that combines two or more sources of energy to power the vehicle, usually an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. There are several types of hybrid vehicles, but the most common is the hybrid electric vehicle (HEV).
In HEVs, the electric motor is powered by a battery charged by regenerative braking and the gasoline engine running. Gasoline engines are smaller and more efficient than conventional gasoline engines. This is because it does not have to provide all the power needed to propel the car. Instead, the electric motor assists the petrol engine when accelerating or when extra power is needed, such as when driving uphill or overtaking other vehicles. When the car stops, the petrol engine shuts off to save fuel and reduce emissions. An electric motor can propel the car at low speeds, such as when driving in a parking lot or in heavy traffic. When the battery charge gets low or more power is needed, the petrol engine kicks in and works with the electric motor to provide the needed power.
Hybrid vehicles typically have a display on the dashboard that shows the driver how much energy is being used and recovered, as well as the battery charge level. Some hybrid vehicles also have a feature called “regenerative braking”, which recovers the energy lost when braking and uses it to charge the battery. This feature significantly increases battery range and reduces fuel consumption.
Simply put, hybrids combine at least one electric motor with a gasoline engine to propel the car, with a system that recovers energy through regenerative braking. Sometimes the electric motor does all the work, sometimes the gas engine does the work, and sometimes they work together. The result is less fuel consumption and therefore less fuel consumption. In some cases, more power can even improve performance.
All power is supplied by a high-voltage battery (separate from the car’s traditional 12-volt battery) and replenished by capturing energy from deceleration that is normally lost to the heat of the brakes in a conventional car. (It does this through a regenerative braking system.) Hybrids also use the gasoline engine to charge and service the battery. Automakers use different hybrid designs to accomplish different tasks, from maximizing fuel economy to minimizing vehicle cost.
This SHVS system consists of the ISG, ECM, Auxiliary Power Module incorporating Lithium-ion battery and a variety of sensors, etc.
Under take-off or acceleration when a lot of fuel is required, the ISG assists the engine to reduce the strain on the engine. Thus, fuel efficiency is improved.
While the vehicle is cruising, the system minimizes the electrical power generation or stops it so that the engine can reduce mechanical load and fuel consumption.
While the vehicle is decelerating, the ISG generates electrical power intensively to charge the lithium-ion battery in the auxiliary power module and the lead-acid battery.
How many Type of Hybrid Vehicles ?
There are several types of hybrid vehicles, including:
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): These vehicles use a combination of gasoline or diesel engines and electric motors to power the vehicle. The electric motor is powered by a battery that is charged by the gasoline or diesel engine and by regenerative braking.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): These vehicles are similar to HEVs but have larger batteries that can be charged by plugging them into an external power source. They can be driven for short distances using only electricity before the gasoline or diesel engine kicks in.
- Extended-Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs): These vehicles are similar to PHEVs but have a larger battery that can power the vehicle for longer distances on electricity alone. When the battery is depleted, a gasoline or diesel engine kicks in to provide power to the electric motor.
- Mild Hybrid Vehicles: These vehicles have a small electric motor that assists the gasoline or diesel engine during acceleration and when extra power is needed, but cannot power the vehicle on its own.
- Full Hybrid Vehicles: These vehicles have a larger electric motor that can power the vehicle at low speeds and assist the gasoline or diesel engine during acceleration and when extra power is needed.
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs): These vehicles use a fuel cell to generate electricity from hydrogen and oxygen, which powers an electric motor. They produce only water vapor as emissions.
Each type of hybrid vehicle has its own unique characteristics and benefits, and the choice of which type to use depends on the specific application and use case.
Parallel mix
In this most common design, an electric motor and a gasoline engine are linked to a common gearbox that mixes the two sources of power. Transmissions can be automatic transmissions, manual transmissions, or continuously variable transmissions (CVT). A very popular hybrid transmission is the power split CVT used in the Toyota Prius and Chevrolet Volt. Transmission type and petrol engine size are key factors in determining the acceleration, sound and feel of a parallel hybrid. Brands using parallel design include Toyota, Lexus, Hyundai, Kia, Ford, Honda, Lincoln, Nissan and Infiniti.
Series hybrid
In this design the electric motor provides all the thrust and there is no physical mechanical connection between the engine and the wheels. The petrol engine is used only for battery charging. The result is an EV-like driving experience with smoother, stronger acceleration. There is usually less vibration when starting a petrol engine. However, this contact does not always coincide with the action of the right foot (remember, the battery creates demand). Therefore, if the car is traveling at a constant speed, the engine may rev up. Some people find this behavior annoying. The BMW i3 with range extender is an example of a serial hybrid.
plug-in hybrid
A plug-in hybrid extends the traditional hybrid concept with a larger battery pack and, like an electric vehicle, must be fully charged externally at a home, office or public charging station. This larger energy store is like a larger gas tank.
Pure electric drive time (24 to 90 km depending on model) is increased and fuel consumption is significantly reduced. In fact, with a short commute and a nightly charge, you’ll be using electricity most of the time. Beyond pure electric range, the car essentially reverts to a traditional parallel hybrid. The Chrysler Pacifica Plug-in Hybrid (above) is an example of a plug-in car.
Plug-in hybrids can be either series or parallel hybrids. No one said it wasn’t complicated.
Advantages Hybrid Car
A hybrid engine has several advantages:
- Better fuel economy:
Hybrid engines are designed to be more fuel efficient than conventional gasoline engines. This is achieved by using an electric motor to assist the petrol engine and reduce the amount of fuel needed to move the car. - Low emissions:Hybrid engines are environmentally friendly as they emit fewer emissions than conventional gasoline engines. Electric motors are battery-powered and emit no emissions, while petrol engines are smaller and more efficient, resulting in lower emissions.
- Regenerative braking:Hybrid engines use regenerative braking. Regenerative braking recovers some of the energy lost when braking and uses it to charge the battery. This feature reduces brake wear and extends battery life.
- More power and torque:A hybrid engine typically combines the power of an electric motor and a gasoline engine to produce more power and torque than a conventional gasoline engine.
- Quiet operation:In pure battery operation, the hybrid motor is almost silent, which can guarantee a more comfortable driving experience.
- Government incentives:Some governments offer incentives such as tax credits and rebates for purchasing hybrid vehicles.
This makes the initial cost of a hybrid vehicle more affordable. Overall, hybrid engine benefits include improved fuel efficiency, lower emissions, regenerative braking, increased power and torque, quieter operation, and government incentives.
Disadvantages Hybrid Car
While hybrid engines have some advantages, they also have potential disadvantages:
- Higher cost:Hybrid vehicles can be more expensive to purchase than conventional gasoline vehicles due to the added technology and components.
- complicated:Hybrid vehicles have more complex systems than conventional gasoline vehicles, which can make repairs more difficult and more expensive if something goes wrong.
- Battery life and replacement cost:Hybrid vehicles use batteries to power the electric motors, but these batteries have a limited lifespan. If the battery needs to be replaced, it can be expensive.
- Limited all-electric range:Most hybrid vehicles have a limited electric-only range, after which the gasoline engine must take over. This can limit the fuel savings and emissions reductions that hybrid vehicles can achieve.
- Higher Weight:Hybrid vehicles are heavier than conventional gasoline vehicles due to the added weight of the electric motor and battery. This can affect performance and handling.
- Limited towing capacity:Hybrid vehicles may have less towing capacity than conventional gasoline vehicles due to their smaller engines.
- Gasoline Dependence:Hybrid vehicles cannot be completely emission-free, as they still need gasoline to power the gasoline engine.
Overall, the disadvantages of hybrid engines include high cost, complexity, high battery life and replacement costs, limited all-electric range, increased weight, limited towing capacity, and reliance on gasoline. I have. However, many of these drawbacks will diminish over time as technology advances and becomes more affordable.
System Architecture
Auxiliary power module incorporates lithium ion battery to supply sufficient power to electrical devices. DC/DC converter is not used.
- ECM includes ENG A-STOP control function. There is no individual ENG A-STOP control module.
- BCM includes keyless start control module.
- BCM, ISG, auxiliary power module and ECM are communicating via CAN bus.
Hybrid System Operation
- Cruising or Engine Automatic Stop State
- Automatic Restart State
- Generation / Regeneration State
- Engine Power Assist State
- Information Display Operation
Cruising or Engine Automatic Stop State
If charging status of lead-acid battery and Li-ion battery is good enough while the vehicle is cruising, ECM stops power generation at ISG. During cruising condition or while the engine is stopped by automatic stop function, lead-acid battery and Li-ion battery supply power to engine electrical devices and body electrical devices listed in “2. System Architecture”.
Cruise or auto-shutdown is a condition in a hybrid vehicle when the gasoline engine automatically shuts down while the vehicle is stationary or at low speeds and the electric motor takes over the vehicle’s propulsion. It is also called idling stop, auto stop start, engine stop start.
Automatic engine shutdown typically works when the car is parked at a traffic light or in heavy traffic, otherwise the petrol engine is idling and wasting fuel. The system uses sensors to recognize when the vehicle has stopped and automatically turns off the engine. As soon as the driver releases his brake pedal, the engine automatically restarts and the car can continue driving. The purpose of automatic engine shutdown is to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by reducing the amount of time the petrol engine is idling and not being used to move the vehicle forward. Hybrid vehicles can save fuel and reduce emissions by using electric motors. This is especially effective in urban traffic that frequently stops and starts.
Overall, automatic drive or engine shutdown is an important feature of hybrid vehicles, helping to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Automatic Restart State
When the engine is restarted after engine automatic stop mode, power is supplied from lead-acid battery to ISG instead of starting motor can start the engine upon request from the ECM incorporating ENG A-STOP control module.
The automatic restart state in a hybrid vehicle refers to an operation of restarting the gasoline engine after it has been stopped during running or from the engine automatic stop state. This state is activated when the driver releases his brake pedal and starts accelerating again.
The hybrid vehicle’s control system uses sensors to monitor the driver’s input to determine when to restart the petrol his engine. As soon as the driver presses his accelerator pedal, the control system activates the petrol engine and puts the vehicle back into normal driving mode.
The purpose of the auto-restart state is to provide the driver with a seamless driving experience where the transition between using the electric motor and using the petrol engine is smooth and discreet. The system is designed to be fast and responsive, so drivers experience no delays or power interruptions.
Overall, the automatic restart condition is an important part of the hybrid vehicle system. This allows the vehicle to seamlessly switch between using an electric motor and a gasoline engine, improving fuel efficiency and reducing vehicle emissions.
Generation / Regeneration State
When the vehicle decelerates under fuel cut condition, ISG utilizes kinetic energy to charge lead-acid battery and Li-ion battery upon request from the ECM.The ECM detects when the brake pedal is depressed to boost the regeneration level.Auxiliary power module sends request to combination meter so that the information display shows power flow
The power generation/regeneration state of a hybrid vehicle means that the electric motor is used to generate electricity while the vehicle is running, and the battery is charged. This state is activated when the driver releases the accelerator pedal and the electric motor switches from using electricity to move the car to acting as a generator.
In this state, the electric motor slows down the car and converts its kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is used to charge the battery. This process is called regeneration. The electricity generated during regeneration is stored in a battery and used to drive the electric motor. The purpose of the generate/regenerate state is to improve the efficiency of the hybrid vehicle powertrain. Using an electric motor for power regeneration allows the vehicle to recover some of the energy lost when braking or decelerating. This energy is later reused to power electric motors and offload gasoline engines for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Overall, the generation/recovery state is an important part of the hybrid vehicle system. This allows the vehicle to recover energy that would otherwise be lost and reuse it to improve overall efficiency.
Engine Power Assist State
When vehicle starts moving or during acceleration, the auxiliary power module supplies power to ISG so that the ISG can assist the crankshaft rotation. This allows for lower engine output to reduce fuel consumption. Power flow indication on the information display is changed.
The engine power assist state in hybrid vehicles refers to the process of using the electric motor to provide additional power and torque to the gasoline engine during acceleration. This state is activated when the driver presses the gas pedal to accelerate the car.
In this state, the electric motor works in tandem with the petrol engine to provide additional power to propel the car forward. The electric motor provides an additional power boost that helps reduce the load on the petrol engine, improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
The purpose of the engine power assist state is to give the driver more power and acceleration while reducing the load on the gasoline engine. By using electric motors to provide additional power, vehicles can accelerate faster and smoother, maintain good fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Overall, engine power assist status is an important part of hybrid vehicle systems. This allows the vehicle to maintain excellent fuel efficiency and reduce emissions while giving the driver improved performance and acceleration.
Information Display Operation
Automatic engine restarting indication is newly added. When the ISG restarts the engine without operating the conventional starting motor, the indication “d” shown above is displayed on the information display.
Information display operation in a hybrid vehicle is to display and manage various information related to the hybrid system and vehicle performance. A hybrid vehicle’s dashboard display provides the driver with important information such as the state of charge of the battery, the fuel efficiency of the vehicle, and the current state of the hybrid system.
By manipulating the information display, drivers can monitor hybrid system performance and adjust driving habits to maximize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. For example, it can show the driver how much energy the electric motor and petrol engine are using and how much energy is being recovered during braking and deceleration.
Information displays may also include features such as eco-driving modes that guide drivers on how to drive more fuel efficiently. The display can also provide real-time feedback on the driver’s driving habits, such as fuel usage and energy recovery.
Overall, information display operations are an important part of hybrid vehicle systems. This allows drivers to monitor vehicle performance and adjust driving habits to maximize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. The information display helps drivers make informed decisions about their driving habits and optimize the performance of their hybrid systems by providing real-time information and feedback.
Input / Output Chart
A/T model with SHVS system is also available.ECM is the main part to control the SHVS system.There is no individual ENG A-STOP control module and DC/DC converter.
ECM and ISG are communicating through CAN bus lines.The terminal C201-3 receives cranking signal from ECM. Its waveform is as shown in the figure above : a. Engine automatic stop state b. Engine automatic restart state c. Engine running state
Component Description
Component Layout



Variations on a Mixed Theme
Twenty years of progress have answered the question, “What is a hybrid?” difficult. For example, Honda’s new hybrid design is not suitable for series or parallel connections. In this design, the engine drives the generator most of the time, like in series hybrids, but sometimes the engine drives the wheels directly, like in parallel hybrids. Then there are the so-called straight-through hybrids, like Volvo’s plug-in hybrids, which use fairly conventional front-wheel drive engines and gearboxes with electric rear axles. The Acura NSX, BMW i8 and Porsche 918 Spyder supercars are similar except that the front wheels are all-electric axles.
mild hybrid
All of the above are considered “full hybrids”. This means that the electric motor can move the car even for short distances. You can’t do it with a “mild” mixture. Like a full hybrid, a mild hybrid’s electric motor assists the petrol engine to improve fuel economy, performance, or both. It also acts as an activator for the automatic start/stop system, turning the engine off when stationary to save fuel.
Mild hybrids were originally intended as an easier and cheaper way to bring hybrid technology to market, but they do not improve fuel economy like full hybrid systems. As such, it never enjoyed the same popularity. More recently, however, mild hybrids have made a comeback, evidenced by the introduction of 48-volt electrical subsystems in vehicles such as the Ram 1500. Essentially, automakers now include mild-hybrid technology in nearly every new model. In the near future, the answer to the question “What is a hybrid car?” will appear. “All” is fine.